Spanning Trees
What is a Spanning Tree?
A spanning tree is a TREE that SPANS a network. That is, a spanning tree is an OVERLAY onto an existing network- it is not literally a network arranged in a tree topology. Any network can be virtually remapped into a tree topology without adding or removing connections, I've provided some convenient examples below.
A Ring Topology
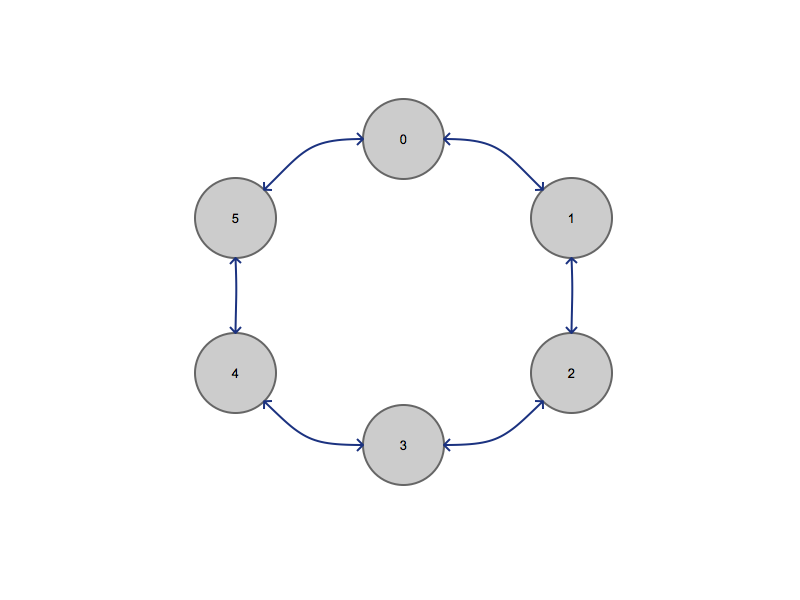
As you can see above, we have a ring topology. This can be easily converted into a a tree topology.
Ring Topology Transformation
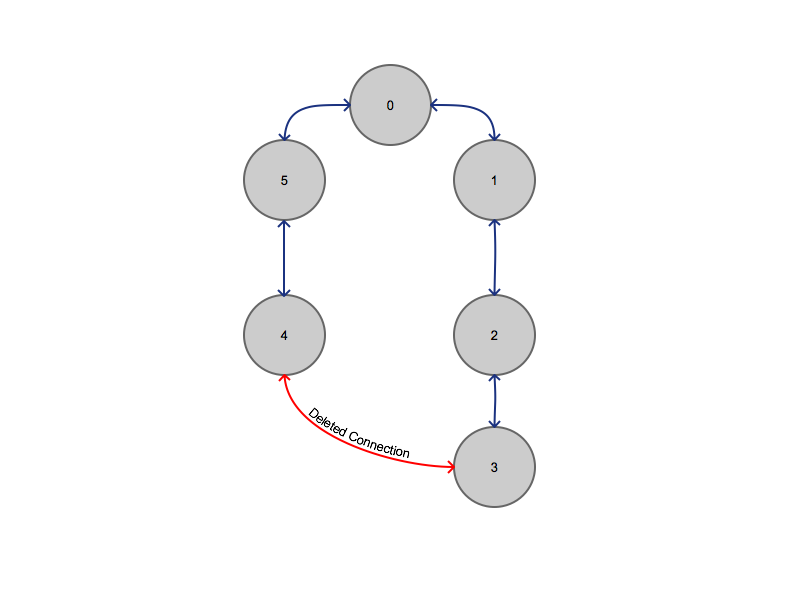
In this case, we have not LITERALLY deleted the connection between nodes 3 and 4. We have only created an abstraction on top of the network - within this abstraction there is no connection between 3 and 4, otherwise the tree would be cyclic.
Some more examples may better demonstrate how spanning trees can be used to avoid cycles within a network and coordinate activities using leader (or root) nodes.
Mesh Topology
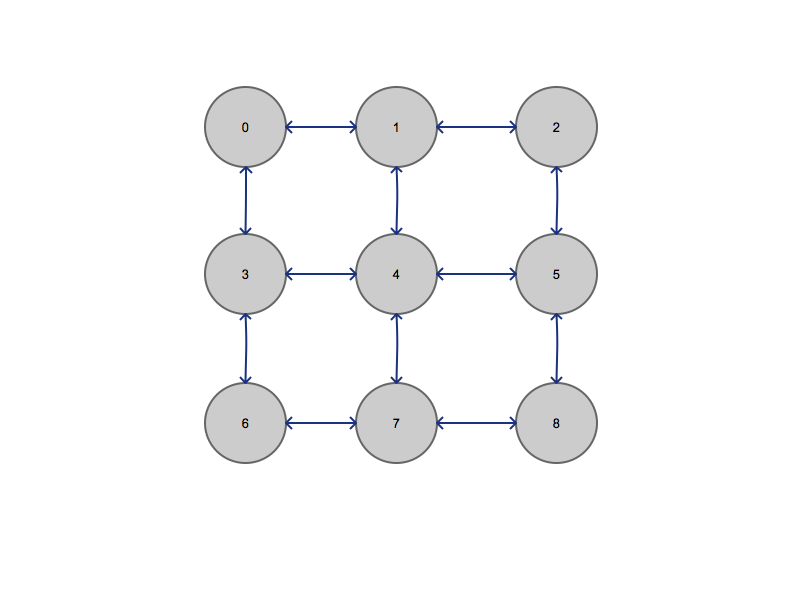
Mesh Topology Transformation
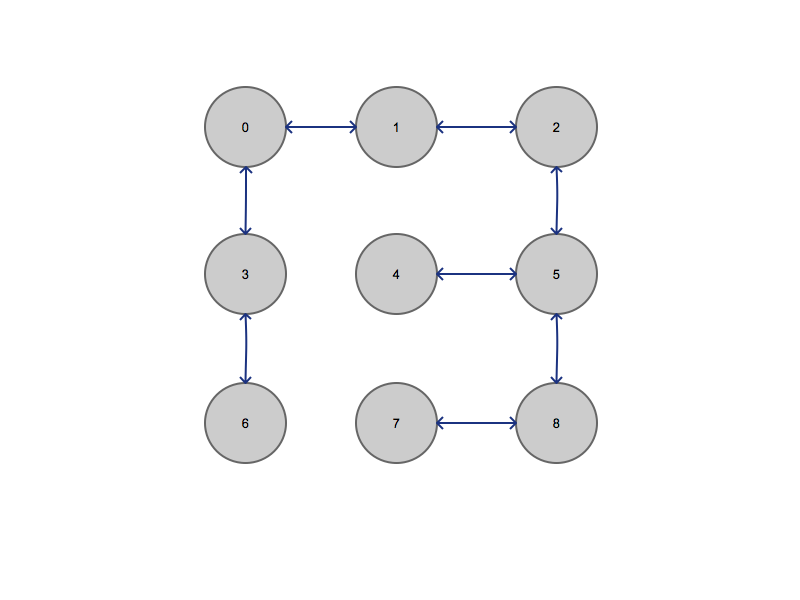
As you can see, even a mesh topology can be transformed into a "tree". Again, in this case we did not actually delete any connections between any nodes, the tree is only a virtual tree. In our virtual tree, the root node is 0, the root node can broadcast and control the network without flooding it with excessive messages - all without having to change the actual topology.
To make it even clearer I've rearranged the nodes into a more traditional tree shape.
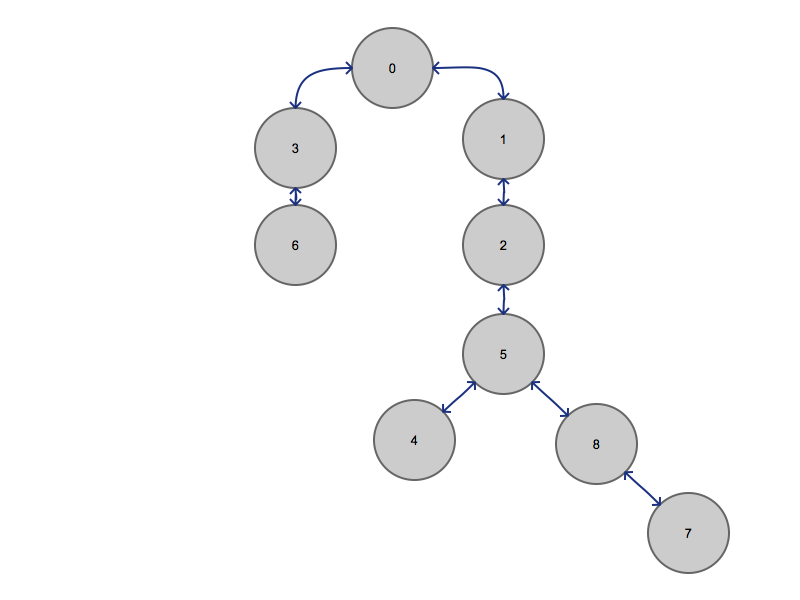
Why does this matter?
Ideally distributed systems should not have a single point of failure. Many times the benefits are going to be increased robustness, decentralization to easily scale etc. Spanning trees are one of the technologies that enable this.
Imagine that we had a network of nodes connected via wireless signal that has intermittent strength. Sometimes connections break down, sometimes there is interference etc. But among these nodes we would like to have some coordinated effort to solve some sort of problem.
There are a number of problems:
- How can we have the leader elected?
- How can we ensure that if the leader, or a section of the graph is unreachable, the system will still continue to function in a degraded state?
The answer is a self-stabilizing spanning tree.
What does it mean to be self-stabilizing?
According to wikipedia: "Self-stabilization is a concept of fault-tolerance in distributed computing. A distributed system that is self-stabilizing will end up in a correct state no matter what state it is initialized with. That correct state is reached after a finite number of execution steps."
What this means in practice is that a self stabilizing system is one that can deal with faults and continue operation.
What does it mean to be a self-stabilizing spanning tree?
If we take both definitions together we can therefore see that a self stabilizing spanning tree must be a spanning tree that overlays on a network that can handle network failure, recovery, and persist operation, even within a degraded state!
What does the election algorithm look like?
The election is based on the the nodes initial value (randomly pre-determined).
The Symbols underneath each node are formatted in the following way:
<Node ID> -> <Root Node, Tree Level (depth), Parent Node>
Root (leader) Nodes are colored green, defective nodes are colored red, all other nodes are colored black.
What does the self-stabilizing spanning tree look like?
The self-stabilizing algorithm looks like this:
The Symbols underneath each node are formatted in the following way:
<Node ID> -> <Root Node, Tree Level (depth), Parent Node>
Root (leader) Nodes are colored green, defective nodes are colored red, all other nodes are colored black.
As you can see, the network periodically has node failures. The node failures represent machine failure, intermittent connectivity failure, etc, for whatever reason that node cannot communicate on the network. Whenever there is a failure, after a certain timeout, a new subnetwork of all reachable nodes is created, and this subnetwork may continue functioning.
Conclusions
Spanning trees are a very powerful tool for leaders within networks to coordinate tasks. Self-stabilizing spanning trees are even more powerful and resilient. I hope you learned something interesting! Thanks for reading!

